
Navigating the complex e-invoicing landscape in individual European countries has become increasingly crucial for businesses operating within the region. Recognizing the complexities arising from diverse e-invoicing models, the European Union is spearheading efforts to create a standardized system for electronic invoicing across the bloc. Let us delve into the latest mandates, legal changes, and harmonization efforts regarding B2B and B2G e-invoicing across Europe, also exploring the diverse e-invoicing standards employed.
Governments across Europe are increasingly recognizing the transformative potential of e-invoicing in improving efficiency, reducing costs, and combating fraud in financial transactions. While approaches vary, many countries are moving towards mandatory e-invoicing for both B2B and B2G transactions, aiming to streamline processes, enhance transparency, and promote digitalization. Some nations have implemented phased mandates to facilitate a smooth transition, while others have enforced strict regulations to accelerate adoption. Overall, there is a growing consensus among European governments on the importance of e-invoicing as a catalyst for modernizing financial practices and fostering economic growth.
Eastern Europe
Here is a list of Eastern European countries:
- Russia
- Poland
- Ukraine
- Romania
- Czech Republic
- Belarus
- Bulgaria
- Slovakia
- Moldova
- Croatia
- Lithuania
- Slovenia
- Latvia
- Estonia
- Serbia
- Montenegro
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Albania
- North Macedonia
- Kosovo
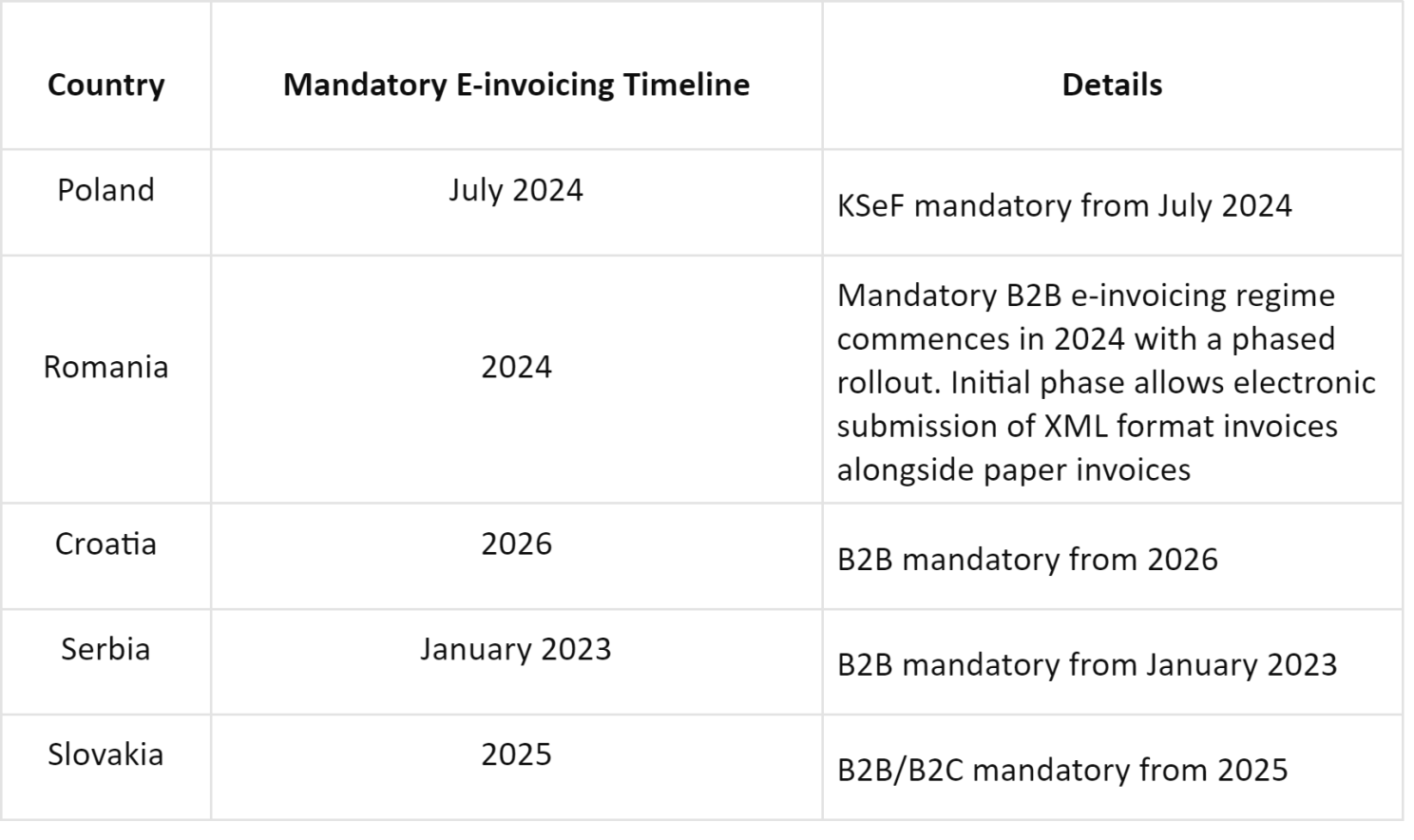
Government’s stance: E-invoicing mandates are prevalent in Eastern Europe, with most countries enforcing mandatory B2G e-invoicing and several transitioning towards mandatory B2B e-invoicing.
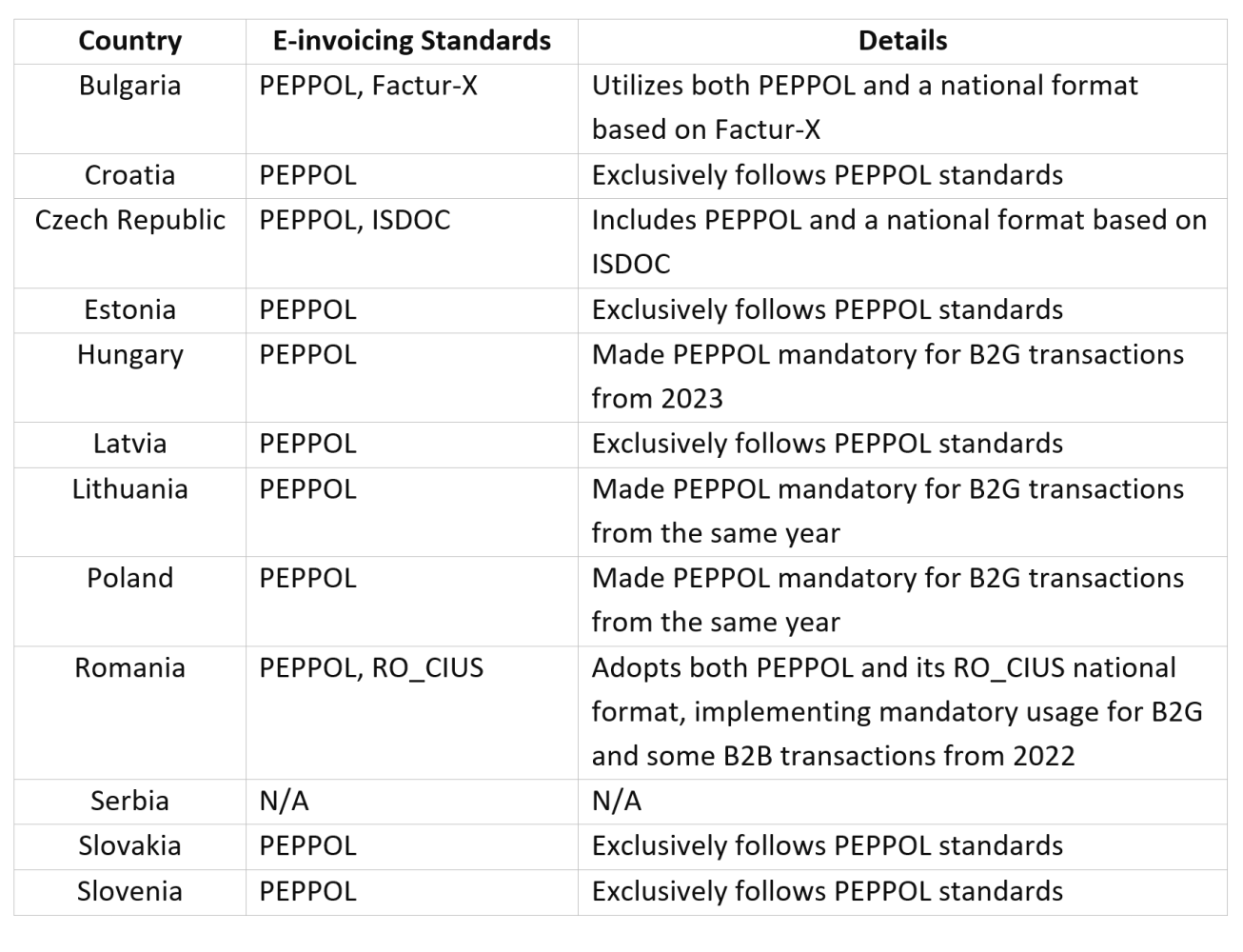
- E-Invoicing Standards
Western Europe
Here is a list of Western European countries:
- Austria
- Belgium
- Finland
- France
- Germany
- Greece
- Ireland
- Italy
- Luxembourg
- Netherlands
- Norway
- Portugal
- Spain
- Sweden
- Switzerland
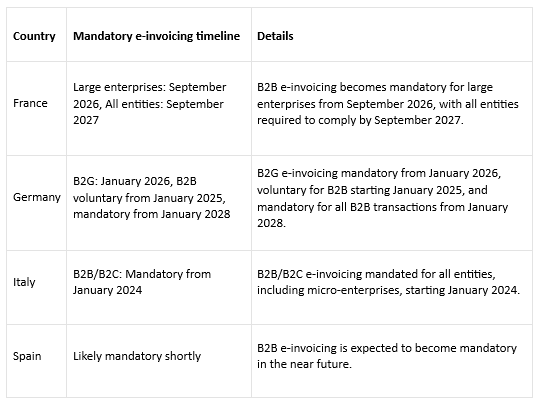
- Government’s stance: In Western Europe, the government’s stance on e-invoicing varies across countries. For instance, countries like France and Germany have implemented phased mandates for Business-to-Business (B2B) e-invoicing, aiming for gradual adoption among businesses. Meanwhile, Italy stands out for its enforcement of mandatory e-invoicing not only for B2B transactions but also for Business-to-Consumer (B2C) interactions. Other countries in the region may have different approaches, with some advocating for voluntary adoption while others opt for stricter regulations. Overall, Western European governments are increasingly recognizing the benefits of e-invoicing in enhancing efficiency, reducing fraud, and promoting digitalization across economic sectors.
- E-invoicing standards: PEPPOL, national formats, and UBL are commonly used.
Northern Europe
- Denmark
- Estonia
- Finland
- Iceland
- Latvia
- Lithuania
- Norway
- Sweden
- Government’s stance: Most countries in Northern Europe have established mandatory B2G e-invoicing and are actively considering or implementing B2B mandates.

- E-invoicing standards: PEPPOL and national formats are widely used.
Southern Europe
- Albania
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Greece
- Italy
- Malta
- Montenegro
- North Macedonia
- Portugal
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Vatican City
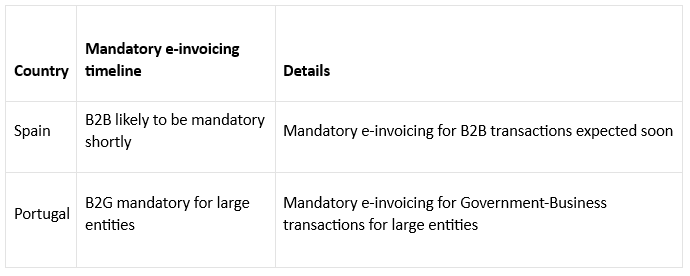
- Government’s stance: Southern Europe exhibits diverse approaches, with Italy enforcing mandatory B2B/B2C e-invoicing, while other countries like Spain and Portugal have B2G mandates and are considering B2B implementation.
- E-invoicing standards: PEPPOL and national formats are commonly used.
Central Europe
- Austria
- Czech Republic
- Germany
- Hungary
- Kosovo
- Poland
- Slovakia
- Government’s stance: While Hungary does not enforce mandatory e-invoicing for B2B or B2C transactions, it requires real-time invoice reporting (RTIR). The Hungarian government aims to improve tax compliance and transparency through RTIR, ensuring that financial transactions are accurately reported to tax authorities in real time.
- Timelines and deadlines: This is not applicable as e-invoicing is not mandatory yet.
- E-invoicing standards: While e-invoices are permitted, they are not mandated. However, if used for B2B transactions, the Hungarian tax authorities require specific data to be reported electronically through the Real-Time Invoice Reporting (RTIR) system. This data can be delivered in an XML file that complies with the latest version (3.0) and can be marked as an e-invoice.
Non-EU
- Government’s stance: The UK encourages B2G e-invoicing but does not enforce mandatory e-invoicing for any transaction type.
The evolving landscape of e-invoicing across Europe reflects a concerted effort by governments to streamline financial processes, enhance transparency, and promote digitalization. While variations exist in mandates and standards, the overarching goal remains the same: to create a unified and efficient e-invoicing ecosystem that benefits businesses, governments, and consumers alike. As the region continues on its digital transformation journey, collaboration and standardization efforts will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of e-invoicing in Europe.
Reach out to us at hello@marmin.ai

