
In Malaysia, the implementation of the e-invoice model via API is set to revolutionize the landscape of business transactions, offering a seamless and efficient approach to invoice generation, submission, and validation. Let’s explore the key features and benefits of this innovative model:
Enhanced Efficiency through API Integration
The API integration streamlines e-invoice submission directly to IRBM, offering taxpayers flexibility through various transmission options to suit businesses of all sizes and technical capabilities:
- Direct Integration: This method allows for seamless integration of a company’s Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system with the MyInvois System. This optimizes the e-invoice generation process by enabling automatic data transfer from the ERP system to IRBM for validation.
- Peppol Service Providers: Businesses can leverage Peppol service providers, a network of certified intermediaries that facilitate secure and standardized e-invoice exchange across diverse platforms. This option benefits companies lacking the resources for direct integration or requiring additional services like data translation.
- Non-Peppol Technology Providers: A range of non-Peppol technology providers offer solutions for e-invoice generation and submission via API. These providers cater to specific business needs and may offer additional features like e-invoice management tools or integration with accounting software.
The IRBM furnishes a Software Development Kit (SDK) incorporating the API configuration guide and endpoints. This comprehensive resource empowers businesses or their technology partners to establish the API connection efficiently, ensuring a smooth transition for e-invoice submission.
Adaptable E-Invoice Formats Supported
The e-invoice structure accommodates a wide spectrum of transactions, encompassing B2B, B2G, and B2C, offering adaptability for businesses of all sizes. Taxpayers can submit e-Invoices in the following formats, adhering to the Universal Business Language Version 2.1 (UBL2.1) data structure:
- Extensible Markup Language (XML): A widely adopted format for representing structured information, recognized for its strict syntax rules. XML is ideal for businesses accustomed to data exchange in this format and possesses the technical expertise to manage potential complexities.
- JavaScript Object Notation (JSON): A lightweight and human-readable format for data interchange, offering enhanced ease of use compared to XML. JSON’s user-friendly structure makes it a preferable choice for businesses seeking a simpler approach to e-invoice generation.
Mandatory Data Fields and Categorization
Issuing an e-invoice requires the completion of 55 mandatory data fields, categorized into eight key areas:
- Address
- Business Details
- Contact Number
- Invoice Details
- Parties
- Party Details
- Payment Info
- Products / Services
In specific instances, additional annexes might be required for submission to IRBM. These annexes may contain supplementary information specific to the transaction, such as customs details for international trade.
A Step-by-Step Guide for Efficient E-Invoice Submission
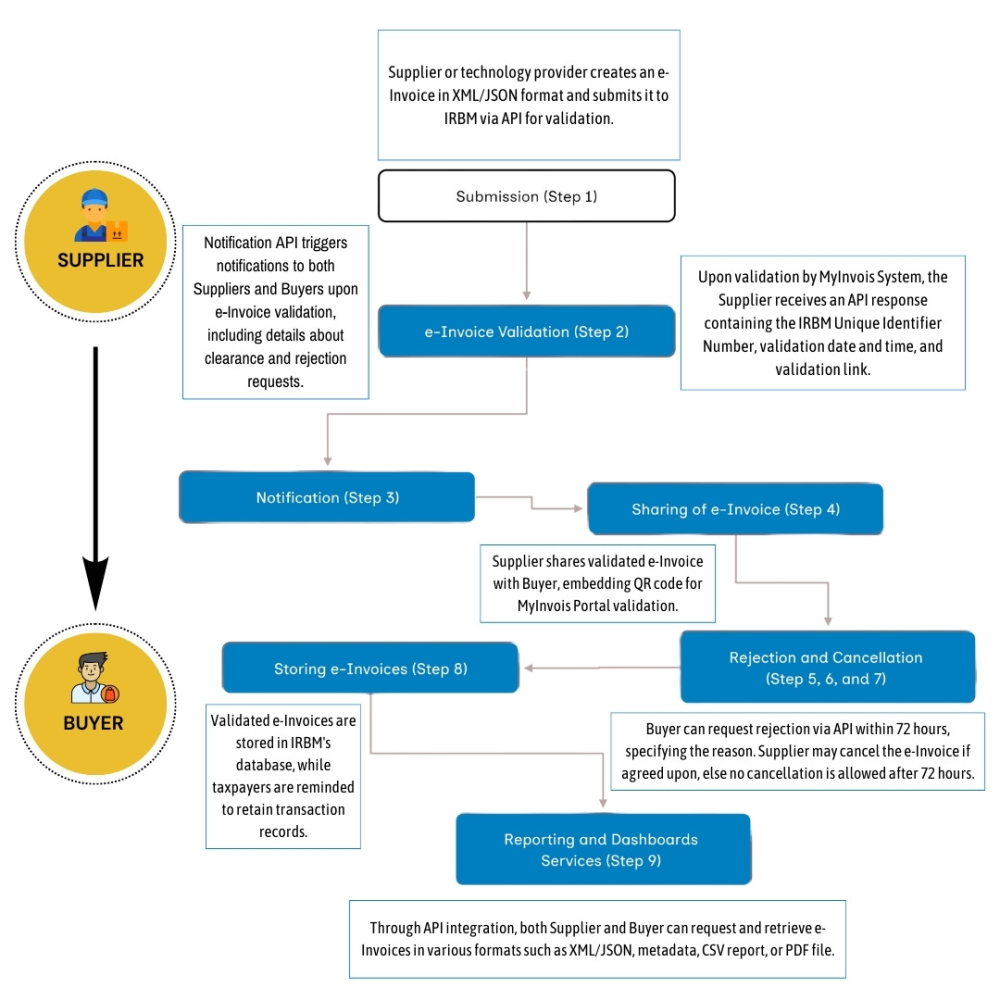
The e-Invoice submission process via API follows a well-defined sequence of steps:
- Pre-Submission Requirements:
- Secure a Digital Certificate: A digital certificate acts as a digital signature that verifies the identity of the e-invoice issuer. This critical security measure helps to prevent fraud and ensure the authenticity of e-invoices submitted to IRBM.
- Prepare Internal Systems or Engage a Technology Provider: Businesses can choose to generate e-Invoices in the mandated format using their internal systems if they possess the necessary technical expertise. Alternatively, they can engage a technology provider specializing in e-Invoice solutions. These providers can handle e-invoice generation, and submission, and potentially offer additional services like data validation and record keeping.
2. Submission and Validation Process
- Submission – Following the completion of a sale or transaction (including adjustments made through e-Invoices), the supplier, or their technology provider, creates an e-Invoice adhering to the UBL2.1 structure in either XML or JSON format. This e-invoice is then submitted to IRBM for validation via API. The supplier must ensure the accuracy of all information included in the submitted e-invoice.
- Validation by IRBM – Upon submission, the MyInvois System performs near real-time validation of the e-invoice. The supplier, or their technology provider, receives an API response containing the following details:
This unique identifier facilitates traceability and reduces the risk of tampering with the e-invoice. An error response will be provided via API if any discrepancies are identified during validation.
3. Notification and Sharing
- Notifications – The MyInvois System incorporates a notification API that automatically sends alerts to both the supplier and the buyer upon successful e-invoice validation. These notifications include details like clearance confirmation and any rejection requests initiated by the buyer. This real-time communication system ensures both parties are promptly informed about the e-invoice status, enabling swift action if necessary.
- Sharing the Validated e-Invoice – Following validation, the supplier is obligated to share the validated e-Invoice with the buyer. If the supplier chooses to share a visual representation of the e-invoice, it must include an embedded QR code. This QR code allows the buyer to verify the e-Invoice’s existence and status directly through the MyInvois Portal.
4. Rejection and Cancellation of an e-invoice
A significant enhancement within the e-invoice model via API is the introduction of functionalities for rejection and cancellation. These features empower both buyers and suppliers with greater control and flexibility in managing the e-invoices, fostering smoother communication and efficient issue resolution.
Understanding Rejection and Cancellation Timeframes
Both buyers and suppliers are granted a 72-hour window following e-invoice validation to initiate rejection or cancellation requests via API. This timeframe allows for timely communication and swift action if discrepancies are identified.
- Buyer-Initiated Rejection: If a buyer detects errors in the e-invoice, such as incorrect quantities, pricing, or tax calculations, they can request a rejection within 72 hours of validation. The rejection request submitted through the API should specify the unique identifier of the e-invoice and the reason for rejection. Upon receiving the notification from IRBM, the supplier can choose to accept the rejection if they acknowledge the validity of the reasons provided.
- Supplier-Initiated Cancellation: In instances where a supplier identifies errors or issues an e-invoice erroneously, they can initiate cancellation within 72 hours of validation through the API. The request body must include the unique identifier of the e-invoice for cancellation.
Example: Leveraging Cancellation for Order Changes
MegaCorp (Supplier) manufactures industrial equipment and supplies them to ABC Engineering (Buyer). Typically, ABC Engineering submits purchase orders outlining the specific equipment and quantities required. MegaCorp utilizes a technology provider to generate e-invoices in JSON format via API.
Following a confirmed order, MegaCorp generates an e-invoice reflecting the agreed-upon details. However, due to unforeseen circumstances, MegaCorp encounters a temporary stock shortage for a specific equipment type included in the original order. Recognizing this issue, MegaCorp proactively cancels the initial e-invoice within the 72-hour window via their technology provider’s API.
Simultaneously, MegaCorp contacts ABC Engineering to explain the stock shortage and propose a revised order with an alternative equipment option or a slight delay for the original equipment. Upon reaching a mutually agreeable solution, MegaCorp issues a new e-invoice reflecting the adjusted order details through the API, which undergoes the standard validation process.
This scenario highlights the benefits of cancellation in situations where:
- Order Modifications are Necessary: The ability to cancel and reissue e-invoices allows for swift adjustments to accommodate changes in orders, preventing potential delays or confusion.
- Proactive Communication: By promptly notifying the buyer of any discrepancies or stock limitations, suppliers can maintain positive business relationships and minimize disruptions.
- Improved Accuracy: Canceling erroneous e-invoices ensures only accurate information is reflected within the system, enhancing data integrity.
The e-invoice model via API streamlines business transactions in Malaysia by offering a secure, efficient, and user-friendly platform for electronic invoice submission. With the recent introduction of rejection and cancellation functionalities, the system empowers both buyers and suppliers with greater control and flexibility in managing e-invoices. By embracing this innovative system, businesses can enhance operational efficiency, ensure data accuracy, and foster seamless communication with trading partners.
Reach out to us at hello@marmin.ai
